What Are Sperm Cramps?
A pain, soreness, or discomfort localised in the testicles or the surrounding area is called sperm cramps, sometimes known as testicular pain or discomfort. The severity and length of these sensations can vary greatly, ranging from minor discomfort that passes quickly to severe and ongoing pain. Although “sperm cramps” is not a medical phrase, it is frequently used colloquially to refer to the pain males may experience in their testicles. Occasionally, depending on the underlying cause, the pain may radiate to the back, groyne, or lower abdomen. It’s important to remember that several illnesses can cause testicular pain, and a diagnosis and appropriate therapy can only be determined after a complete evaluation by a healthcare professional. Common Symptoms One or both testicles may experience a continuous agonising or throbbing pain that may spread to the back, groyne, or lower abdomen. This condition is known as testicular pain or sperm cramps. Physical activities like walking, running, or sexual activity can aggravate the discomfort caused by swelling or tenderness in the testicles and surrounding tissues. Tumours or masses may also be present, along with discernible changes in the texture of the testicles, such as being softer or more complex. Furthermore, fever or flu-like symptoms may accompany discomfort that spreads to other places, suggesting an infection or inflammation that must be treated immediately to avoid complications.Causes Of Sperm Cramps
A pain, soreness, or discomfort localised in the testicles or the surrounding area is called sperm cramps, sometimes known as testicular pain or discomfort. The severity and length of these sensations can vary greatly, ranging from minor discomfort that passes quickly to severe and ongoing pain. Although “sperm cramps” is not a medical phrase, it is frequently used colloquially to refer to the pain males may experience in their testicles. Occasionally, depending on the underlying cause, the pain may radiate to the back, groyne, or lower abdomen. It’s important to remember that several illnesses can cause testicular pain, and a diagnosis and appropriate therapy can only be determined after a complete evaluation by a healthcare professional. Individual experiences may vary, and consulting with a healthcare specialist is advisable for a proper diagnosis and tailored treatment.Infection
Infections, such as epididymitis or prostatitis, can induce sperm cramps by triggering inflammation in the reproductive organs. Inflammatory responses may disrupt normal muscle and nerve function. Abnormality in nerve & muscle functioning may lead to discomfort during ejaculation.2. Testicular issues:
Testicular problems, like varicocele or testicular torsion, may cause sperm cramps. These conditions can compromise blood flow to the testicles. They are ultimately impacting their function and inducing pain during ejaculation. Any testicular abnormality is the ultimate cause of semen cramps.3. Muscle tension:

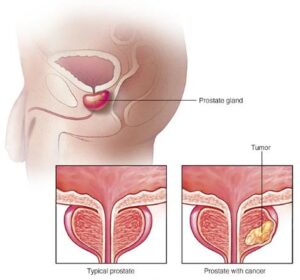
4. Prostate issues:


POIS is a rare condition where individuals experience flu-like symptoms, including cramps, after ejaculation. The exact cause is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve an allergic or autoimmune response to components of semen.
6. Psychological factors:






Practical Solution for Sperm Pain
Sperm cramps require a variety of effective treatments to relieve pain and address the source. Antibiotics for epididymitis and prostatitis and painkillers for acute pain are advised. Lifestyle adjustments involve eating well, staying hydrated, and exercising regularly, which support general health and minimise cramping. Home therapies like warm compresses and mild stretching can relieve pain immediately by relaxing and increasing blood flow. Meditation and counselling can also reduce psychological variables that worsen symptoms. These diverse measures can help people control sperm cramping, improve their quality of life, and avoid consequences.Medical Treatments
The goals of sperm cramp medical therapies are to relieve symptoms and address underlying causes successfully. When bacterial causes of inflammation and pain are found, such as in the case of prostatitis or epididymitis, antibiotics are recommended. For the treatment of acute discomfort, painkillers like NSAIDs are frequently utilised. Muscle relaxants may be recommended in situations where pelvic tension contributes to cramping. If a varicoceles issue causes substantial pain or interferes with fertility, surgical treatments, including varicocelectomy, might be required. Follow-up care includes preventing problems or recurrence, adjusting medication as needed, and assessing treatment efficacy. The appropriate diagnosis and management of sperm cramps necessitate medical attention, and each treatment plan is customised to the patient’s unique situation and health requirements.Lifestyle Changes
The goals of sperm cramp medical therapies are to relieve symptoms and address underlying causes successfully. When bacterial causes of inflammation and pain are found, such as in the case of prostatitis or epididymitis, antibiotics are recommended. For the treatment of acute discomfort, painkillers like NSAIDs are frequently utilised. Muscle relaxants may be recommended in situations where pelvic tension contributes to cramping. If a varicoceles issue causes substantial pain or interferes with fertility, surgical treatments, including varicocelectomy, might be required. Follow-up care includes preventing problems or recurrence, adjusting medication as needed, and assessing treatment efficacy. The appropriate diagnosis and management of sperm cramps necessitate medical attention, and each treatment plan is customised to the patient’s unique situation and health requirements.Home Remedies
A natural and accessible approach to reducing pain and enhancing well-being is the main focus of home treatments for sperm cramps. Stretching gently can help release tension and increase flexibility while applying warm compresses can calm muscles and promote blood flow. Exercise strain can be minimised by donning supportive pants, and pain can be eased and muscles relaxed by taking an Epsom salt bath. It is possible to lessen inflammation by drinking plenty of water and eating a diet high in berries, leafy greens, and omega-3 fatty acids and reducing stress on the testicles by avoiding activities and benefiting from the anti-inflammatory qualities of herbal medicines such as ginger tea or chamomile tea. For the correct diagnosis and treatment of severe or persistent testicular discomfort, even though these therapies can help, seeing a healthcare professional is still necessary.Stress Management
Sperm cramps can increase physical symptoms and discomfort; thus, managing stress is essential for treating them. Efficient approaches comprise stress-reduction and nervous system-calming procedures such as progressive muscle relaxation, deep breathing, and meditation. Exercises that increase endorphin release and lower stress hormones include jogging, yoga, and walking. Another way to reduce stress is to eat a balanced diet, sleep well, and manage time effectively. In addition to cognitive-behavioural therapy and mindfulness exercises, which help reframe unfavourable ideas, strong social ties and asking friends, family, or support groups for assistance also bring emotional comfort. Expert assistance, such as counselling or stress-reduction plans, provides extra techniques and encouragement for stress management, eventually enhancing general health and lessening the frequency and severity of sperm cramp incidence.Sperm Cramps Symptoms
Testicles, the scrotum, the lower abdomen, the groyne, and the lower back can all be affected by sperm cramps, which are also referred to as testicular or scrotal pain. The pain can range in intensity from subtle aches to acute pains. These cramps may be intermittent or continuous, accompanied by tenderness, swelling, and pain during ejaculation. Occasionally, they may also cause symptoms related to the urine, such as burning or frequent urination. These symptoms might damage one’s emotional health and cause anxiety or discomfort, in addition to impairing daily comfort and physical activity. It is essential to identify these symptoms and seek medical attention as soon as possible because they may point to underlying issues that need particular therapies or management techniques.Descriptions of Typical Symptoms
A dull aching or severe pain that might radiate to the lower back or belly is what is known as sperm cramps, which are defined by pain in the testicles or scrotum. The pain could be sporadic or chronic, affecting everyday tasks and emotional stability. Pneumonia: scorching or frequent urination is occasionally experienced, along with swelling, soreness, and discomfort during ejaculation. Early detection of these symptoms is crucial for prompt medical examination and proper treatment, as they can cause substantial pain and interfere with regular functioning. In addition to helping you manage any acute discomfort, knowing what these symptoms mean will help you rule out any underlying illnesses that may need specialised treatments or lifestyle changes to avoid or relieve long-term issues.Pain Location and Intensity
Sperm cramp sufferers and medical professionals diagnosing the ailment must know the location and severity of the pain. Usually located in the scrotum or testicles, this discomfort may radiate to the lower back, groyne, or belly, indicating that nearby structures, such as the epididymis, may be affected. There is a wide range in pain intensity, from subtle or mild discomfort to intense, severe pain that interferes with everyday functioning and emotional stability. Several factors, including personal pain thresholds and the underlying cause, such as inflammation, infection, or injury, determine pain intensity. Accurately determining where pain is occurring and gauging its severity help determine the best course of treatment to manage any underlying issues and relieve symptoms properly.Duration and Frequency
An important clue to the pattern and severity of the illness is the length and frequency of sperm cramping. What is meant by duration is the length of time that each pain episode lasts; it can range from brief discomfort to protracted episodes that continue for hours or days. Factors including the underlying reason, the degree of inflammation, and the patient’s reaction to the therapies can all affect this variability. In contrast, frequency denotes the frequency of these episodes, ranging from infrequent occurrences to frequent and regular pain episodes. The assessment of sperm cramping’ chronicity and the formulation of effective management plans are facilitated by an understanding of these factors. Healthcare professionals can more effectively adapt therapies to relieve symptoms and address any underlying conditions causing discomfort by keeping track of changes in duration and frequency across time.Associated Symptoms
Associated symptoms accompanying sperm cramps provide additional insights into the condition and its impact on daily life and reproductive health: Swelling Swelling in the affected testicle or scrotum is a common accompanying symptom of sperm cramps. This swelling can vary in severity and may contribute to the overall discomfort and tenderness experienced in the area. It often indicates inflammation or fluid buildup, which may be caused by underlying infections, trauma, or other medical conditions affecting the reproductive organs. Discomfort During Ejaculation Many men with sperm cramps report increased pain or discomfort during ejaculation. This symptom can significantly affect sexual function and pleasure, potentially leading to anxiety or avoidance of sexual activity. Discomfort during ejaculation may stem from inflammation or sensitivity in the reproductive organs, exacerbated by the physiological changes and muscle contractions involved in ejaculation. Urinary Symptoms Some individuals experiencing sperm cramps may also notice urinary symptoms such as frequent urination, a burning sensation while urinating, or difficulty urinating. These symptoms can indicate involvement of the urinary tract, such as a urinary tract infection (UTI) or other urological issues that may contribute to or exacerbate the pain and discomfort. Tenderness and Sensitivity The affected testicle or scrotum may feel tender to the touch, especially during pain or inflammation. This tenderness can make physical activities, such as walking or sitting, uncomfortable and may necessitate adjustments in daily routines to minimize discomfort. Visible Changes In some cases, sperm cramps may be accompanied by visible changes in the scrotum or testicles, such as redness, warmth, or the presence of palpable lumps. These changes can provide additional clues to the underlying cause of the pain and may prompt further investigation or diagnostic testing.1. Can sperm buildup cause pain?
Yes, sperm buildup in the body can cause pain. Its effects go beyond the pain alone. Its buildup in the body can lead to prostate problems and even prostate cancer. The loss of sperm from the body is as important as its production.
2. Why do I have cramps but no period?
Possible reasons for cramps without a period include ovulation, stress, hormonal fluctuations, pregnancy, pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and endometriosis. Consult a healthcare professional for a thorough examination and appropriate guidance. 3. Can you feel cramps when sperm meets egg? Yes, you can feel cramps when sperm meets eggs. Some women may experience mild cramping or discomfort during ovulation, which is when the egg is released from the ovary. This sensation is unrelated to the moment of fertilization itself. Additionally, it’s important to note that not every woman will feel ovulation cramps. It can be an early sign of fertilization of an egg by sperm and usually occurs after 5–6 hours of fertilization. 4. Does every boy get sperm cramps? No, not every boy gets sperm cramps. It is a little-known phenomenon. Certain lifestyle habits and underlying medical conditions can contribute to post-ejaculatory pain. However, if you are not having sperm cramps, it’s nothing to be worried about. 5. Is it bad to waste sperm? No, it’s not bad to fritter away sperm. It’s an essential process. The accumulation of sperm may cause prostate cancer. It’s mandatory to waste sperm; otherwise, our body does this by itself in the form of nightfall. 6. Is removing sperm daily good for you? Some studies suggest a potential link between frequent ejaculation and reduced prostate cancer risk. However, more research is needed. Removing sperm daily is good for prostate health and reduces the chances of prostate cancer by 90%. Regular ejaculation may improve sperm motility. However, every picture has a dark side as well. Weakness, tiredness, lack of interest, and loss of confidence can result from over-loss of sperm. Do it, but don’t become addicted to it. 7. How many times should a gym man release sperm in a week? 2-3 times a week is recommended. If you do so, the main focus of testosterone will be on building muscle and less on restoring a normal sperm count. However, from person to person, it varies. Some people have good control and can even work out for weeks without wasting sperm at all. 8. What exercises produce more sperm? Cardiac exercises and weight resistance are the best exercises to boost sperm production and increase fertility. Exercises like competitive cycling, swimming, and triathlons should also be included in the routine to reduce the chances of prostate problems.Conclusion :
Sperm cramps, also known as post-ejaculatory pain, are a discomfort or pain in the testicles, lower abdomen, or genitals that some men experience after ejaculation.
The exact cause is unknown, but potential contributors include infection, muscle tension, prostate issues, and psychological factors.
Symptoms can range from mild discomfort to severe pain and may also include pain in the groin, back, or legs. If you experience sperm cramps, it’s important to see a doctor to rule out any underlying medical conditions and discuss treatment options.
References: https://googlescholars.com https://en.wikipedia.org https://www.quora.com/



[…] Sperm Cramps-Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Remedies & FAQs […]
[…] Sperm Cramps-Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Remedies & FAQs […]
[…] Sperm Cramps-Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Remedies & FAQs […]
[…] Sperm Cramps-Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Remedies & FAQs […]